CWTS - Certified Wireless Technology Specialist
Given by Certified Wireless Network Expert (CWNE) #1, who founded the Certified Wireless Network Professional (CWNP) Program, the Certified Wireless Technology Specialist (CWTS) is a certification that validates the knowledge and skillset of IT sales and support professionals on the basics of Enterprise 802.11 wireless networks. This comprehensive certification was designed to prove your understanding of Wi-Fi technology and pre-requisite data networking and to help put you on a track to continued success in the industry.
Day 1 - 2 Introduction (Basic Routing and Switching)
In this broad-based foundational course, Devin Akin will take you through the basics of networking devices, management systems, protocols, routing & switching, and common security threats and solutions. You will experience demonstrations of a broad scope of networking devices and diagnostic tools. Attending this course will prepare you to tackle networking tasks such as design, installation, configuration, and troubleshooting.
Chapter 1: The OSI Model
- OSI Model Layers, Physical Layer, Data Link Layer, Network Layer, TCP/IP Model
- Transport Layer, Ports, TCP, UDP, Session and Presentation Layers, Application Layer, Peer Communication, Encapsulation
Chapter 2: Device Addressing
- Mac, IP, Local Addressing
- Packet Structure, Subnetting
- Host, Broadcast and Network
- Default Gateway, IP, Subnet, Public vs. Private Addresses
Chapter 3: Switching
- Ethernet Hub, Switch, Bridge
- Virtual LANs
Chapter 4: IPv4 Routing
- Routing, Router Interfaces, Routing Table
- Routing Protocols, Routing in SOHO and SMB, Diagnostics
Chapter 5: Internet Gateways
- SOHO and SMB, Gateways, NAT, PAT
- Port Redirection and DMZ Ports, Virtual Servers, VPN, Load Balancing
- SPI Firewall Features, Inter-VLAN Routing
Chapter 6: Network Protocols
- TCP, UDP, DHCP
- DNS, NTP
- NTP, TFTP, SYSLOG, FTP
- FTP, WebDAV, RTSP, RTP, SSH2 and Telnet
Chapter 7: Device Management And Security Threats
- Firewalls, Default Passwords, Insecure Management Protocols, Insecure Virtual Servers, Console Ports
Chapter 8: Device Management And Internet Bandwidth
- Internet Bandwidth Per User, Local Storage, Cloud Storage, Cloud Backups
- Streaming and Social Media, Consumer Electronics, Computing Devices, Application Layer Visibility and Control (AVC)
Chapter 9: Device Management
- Device Management, Environmental Conditions, Cables and Cable Management, Console Ports
- Transport Layer, Ports, TCP, UDP, Session and Presentation Layers, Application Layer, Peer Communication, Encapsulation
Chapter 10: Troubleshooting
- Diagnostic Tools, Rogue DHCP Servers, IP Address Conflicts
- Packet Structure, Subnetting
Day 3 - 4 CWTS - Certified Wireless Technology Specialist
The CWTS certification is a sales & support level wireless LAN certification for the Certified Wireless Network Professional (CWNP) Program. To earn a CWTS certification, you must take the exam at a Pearson Vue Testing Center and pass with a score of 70% or higher. Instructors must pass with a 80% or higher. The CWTS is a lifetime certification. Because CWTS is an entry-level certification, no re-certification is required.
Course Outline
Wireless Technologies, Standards, and Certifications
1.1 Define the roles of the following organizations in providing direction and accountability within the wireless networking industry
- IEEE
- Wi-Fi Alliance
- Local regulatory authorities
1.2 Define basic characteristics of and concepts relating to Wi-Fi technology
- Range, coverage, and capacity
- Frequencies/channels used
- Channel reuse and co-location
- Infrastructure and ad hoc modes
- BSSID, SSID, BSS, ESS, BSA, IBSS
- Network discovery via active and passive scanning
- 802.11 authentication and association
- Data rates and throughput
- The distribution system and roaming
- Protection Mechanisms
- Power saving operation
- Dynamic rate switching
1.3 Summarize the basic attributes of the following WLAN standards, amendments, and product certifications
- 802.11a
- 802.11b
- 802.11g
- 802.11n
- Wi-Fi Multimedia (WMM) certification
- WMM Power Save (WMM-PS) certification
- Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA/WPA2) certification
- Enterprise
- Personal
1.4 Explain the role of Wi-Fi as a network access technology
- WPAN, WLAN, WMAN, WWAN
- The OSI reference model
Hardware and Software
2.1 Identify the purpose, features, and functions of the following wireless network components. Choose the appropriate implementation or configuration steps in a given scenario.
- Access Points
- Controller-based
- Autonomous
- Cooperative
- Mesh
- Wireless LAN Routers
- Wireless Bridges
- Wireless Repeaters
- WLAN Controller
- Distributed and centralized data forwarding
- Power over Ethernet (PoE) Devices
- 802.3af and 802.3at
- Midspan
- Endpoint
2.2 Identify the purpose, features, and functions of the following client device types. Choose the appropriate installation or configuration steps in a given scenario.
- PC Cards (ExpressCard, CardBus, and PCMCIA)
- USB2
- PCI, Mini-PCI, and Mini-PCIe, and Half Mini PCIe cards
- Workgroup Bridges
- Client utility software and drivers
2.3 Identify the purpose, features, and proper implementation of the following types of antennas.
- Omni-directional / dipole
- Semi-directional
- Highly-directional
2.4 Describe the proper locations and methods for installing RF antennas
- Internal and external (to the AP) antennas
- Pole/mast mount
- Ceiling mount
- Wall mount
Radio Frequency (RF) Fundamentals
3.1 Define the basic concepts and units of RF measurements, identify when they are used, and perform basic unit conversion.
- Watt (W) and milliwatt (mW)
- Decibel (dB)
- dBm
- dBi
- RSSI
- SNR
3.2 Identify and explain RF signal characteristics
- Frequency
- Wavelength
- Amplitude
- Phase
3.3 Identify factors which affect the range and rate of RF transmissions
- Line-of-sight requirements
- Interference (Wi-Fi and non-Wi-Fi)
- Environmental factors, including building materials
- Free Space Path Loss
3.4 Define and differentiate between the following physical layer wireless technologies
- 802.11b HR/DSSS
- 802.11g ERP
- 802.11a OFDM
- 802.11n HT
3.5 Define concepts which make up the functionality of RF spread spectrum communication
- 802.11 channels
- Co-location of 802.11a/b/g/n systems
- Adjacent-channel and co-channel interference
- WLAN / WPAN co-existence
- CSMA/CA operation
- Half duplex communications
3.6 Understand and apply basic RF antenna concepts
- Passive Gain
- Beamwidth
- Simple diversity
- Polarization
3.7 Identify the use of the following WLAN accessories and explain how to select and install them for optimal performance and regulatory domain compliance
- RF cables
- RF connectors
- Lightning Arrestors and grounding rods
Site Surveying and Installation
4.1 Understand and describe the requirements to gather information prior to the site survey and do reporting after the site survey
- Gathering business requirements
- Interviewing stakeholders
- Gathering site-specific documentation including existing network characteristics
- Identifying infrastructure connectivity and power requirements
- Understanding RF coverage requirements
- Understanding application requirements
4.2 Define and differentiate between the following WLAN system architectures and understand site survey concepts related to each architecture. Identify and explain best practices for access point placement and density.
- Multiple Channel Architecture (MCA)
- Single Channel Architecture (SCA)
4.3 Describe the primary purpose and methodology of manual and predictive site surveys
4.4 Define the need for and the use of a manual site survey tool and differentiate between the following manual site survey types
- Active surveys
- Passive surveys
4.5 Differentiate between manual and predictive site surveys
- Advantages and disadvantages of each site survey methodology
4.6 Define the need for and use of site survey software or a protocol analyzer in a manual site survey as it relates to identifying, locating, and assessing nearby WLANs
4.7 Differentiate between site survey methods for indoor and outdoor wireless service
4.8 Define the need for and use of a spectrum analyzer in a site survey
- Identification and location of interference sources
- Differentiation of Wi-Fi and non-Wi-Fi interference sources
4.9 Understand industry best practices for optimal use of directional and omni-directional antennas in site surveys
Applications, Support, and Troubleshooting
5.1 Identify deployment scenarios for common WLAN network types and suggest best practices for these scenarios.
- Small Office / Home Office (SOHO)
- Extension of existing networks into remote locations
- Building-to-building connectivity
- Public wireless hotspotsCarpeted office, education, industrial, and healthcare
- Last-mile data delivery – Wireless ISP
- High density environments
5.2 Recognize common problems associated with wireless networks and their symptoms, and identify steps to isolate and troubleshoot the problem. Given a problem situation, interpret the symptoms and the most likely cause.
- Throughput problems
- Connectivity problems
- RF coverage or capacity problems
- Interference from Wi-Fi or non-Wi-Fi sources
- Application performance problems
- RF performance problems, such as multipath and hidden nodes
5.3 Identify procedures to optimize wireless networks.
- Infrastructure hardware selection and placement
- Identifying, locating, and removing sources of interference
- Client load-balancing and infrastructure redundancy
- Analyzing infrastructure capacity and utilization
Security & Monitoring
6.1 Identify and describe the following legacy WLAN security technologies.
- SSID Hiding
- WEP
- MAC Filtering
6.2 Understand the basic operation of and implementation best practices for the following WLAN security technologies.
- WPA- and WPA2-Personal
- WPA- and WPA-2 Enterprise
- 802.1X/EAP
- AAA and RADIUS
- Encryption – TKIP/CCMP
6.3 Understand the basic functions and implementation best practices for the following WLAN
security technologies.
- Role Based Access Control (RBAC)
- Virtual Private Networking (VPN)
- Wireless Intrusion Prevention Systems (WIPS)
- Captive Portals
- Network management and monitoring systems
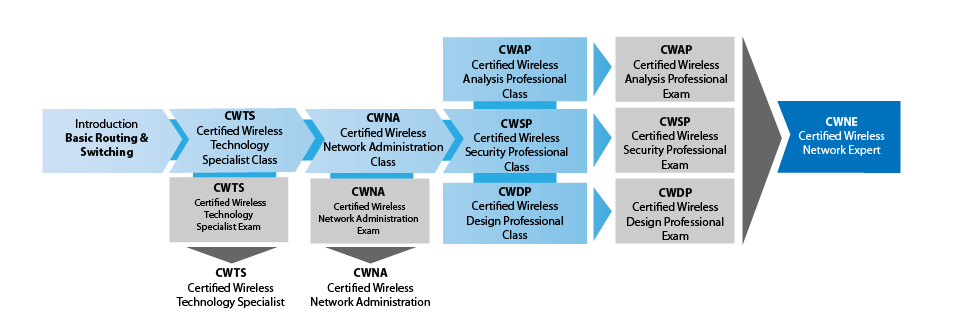
Wireless Certification Road Map
About the Instructor
Devin Akin is the founder of Divergent Dynamics, a Wi-Fi Systems Integrator, Value-Added Reseller (VAR), and Training organization. He specializes in innovative performance optimization solutions for a variety of high-density scenarios in several markets. Mr. Akin was named to the TWW Top 100 Wireless Technology Experts list for 2014.
Akin has over 20 years experience in IT, with 15 years in WLAN specifically. Over the last 6 years, he has held top executive positions with WLAN hardware market leaders, such as Aerohive Networks and AirTight Networks.
Akin got his start working as a network design engineer for EarthLink, AT&T/BellSouth, Foundry Networks, and Sentinel Technologies as well as working as an RF engineer in the U.S. Army. He then went on to co-found Certified Wireless Network Professional (CWNP), now the de facto global standard for vendor-neutral Wi-Fi training and certifcation, and Peachtree Wireless Solutions, a vendor-specifc training and services company; he served as CTO for both companies until 2009.
He has authored and edited several books with Wiley-Sybex and McGraw-Hill and holds some of the industry’s most esteemed certifications, including Certified Wireless Network Expert (CWNE). He is considered an authority on Wi-Fi technology and the Enterprise Wi-Fi market at-large.